If you are a Mac admin you might have noticed some Apple plists are more complex than others these days. As evidenced in my post Don’t Be a Jerk, getting the status of Do Not Disturb in Big Sur was a multi-step exercise. Check out this modified code excerpt from doNotDisturb‘s Big Sur handling
#!/bin/sh
#Big Sur DnD status, returns "true" or [blank] (to be run as console user)
dndStatus="$(/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "print :userPref:enabled" /dev/stdin 2>/dev/null <<< "$(plutil -extract dnd_prefs xml1 -o - /dev/stdin <<< "$(defaults export com.apple.ncprefs.plist -)" | xmllint --xpath "string(//data)" - | base64 --decode | plutil -convert xml1 - -o -)")"
#if we have ANYTHING it is ON (return 0) otherwise fail (return 1)
[ -n "${dndStatus}" ] && { echo ON; exit 0; } || { echo OFF; exit 1; }
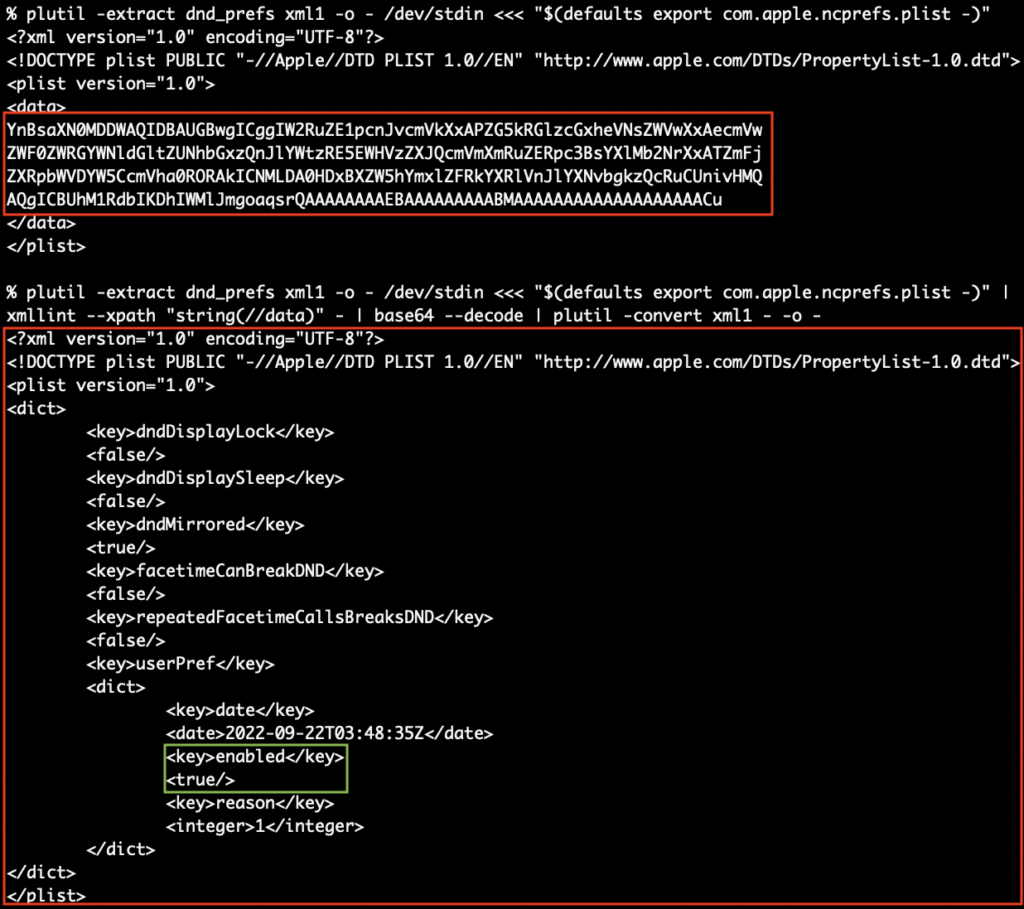
Why is it so complex? Well because with the user preference domain of com.apple.ncprefs there is a base64 encoded plist embedded in the dnd_prefs key and requires some massaging to get it to a state where PlistBuddy can read and then extract the status from the :userPref:enabled key. See it’s just that easy! 😅
In macOS Monterey and higher Apple is now using JSON for Focus status which is great because it can can be parsed much easier (perhaps using my ljt or jpt tools) but sometimes not even that is needed! Sometimes file presence or awking is sufficient to get a reliable result too. See the evolution of doNotDisturb.sh for macOS for the myriad techniques one can use.
Now, here we are at Monterey on the verge of Ventura and not all areas of macOS have seen the JSON light and are still using nested base64-encoded Plist blobs to store the states of new features like iCloud Private Relay but luckily not the per interface setting of Limit IP Tracking.
iCloud Private Relay Status
Now why would you want to know these statuses? Perhaps you have a VPN product that doesn’t work when Private Relay is turned on or if Limit IP Tracking is turned on for a particular interface and you need to alert the user. Additionally maybe there’s an issue if your VPN browser handshake fails when Safari is used, if so see: Determining URL scheme handlers in macOS. Back to the task at hand though let’s turn some prefs inside out and look at iCloud Relay status with iCloudPrivateRelayStatus.sh
#!/bin/bash
: <<-LICENSE_BLOCK
iCloud Private Relay Status Checker (20250204) - (https://github.com/brunerd)
Copyright (c) 2025 Joel Bruner (https://github.com/brunerd)
Licensed under the MIT License
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
LICENSE_BLOCK
#############
# FUNCTIONS #
#############
#include this self-contained function in your script
function iCloudPrivateRelay()(
#only for Moneterey and up, 11 and under need not apply
[ "$(sw_vers -productVersion | cut -d. -f1)" -le 11 ] && return 1
#parent pref domain
domain="com.apple.networkserviceproxy"
#key that contains base64 encoded Plist within parent domain
key="NSPServiceStatusManagerInfo"
#path within base64 embedded plist, there are multiple PrivacyProxyServiceStatus entries but this one seems primary
targetPath=':$objects:1:PrivacyProxyServiceStatus'
#get the top level data from the main domain
parentData=$(launchctl asuser "$(stat -f %u /dev/console)" sudo -u "$(stat -f %Su /dev/console)" defaults export "${domain}" -)
#if domain does not exist, fail
[ -z "${parentData}" ] && return 1
#export and decode the base64 data as plist XML and look for
keyStatusCF=$(/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "print '${targetPath}'" /dev/stdin 2>/dev/null <<< "$(plutil -extract "${key}" xml1 -o - /dev/stdin <<< "${parentData}" | xmllint --xpath "string(//data)" - | base64 --decode | plutil -convert xml1 - -o -)")
#if no value, fail
[ -z "${keyStatusCF}" ] && return 1
#if true/1 it is on, 0/off (value is integer not boolean BTW)
[ "${keyStatusCF}" = "1" ] && return 0 || return 1
)
########
# MAIN #
########
#example - multi-line if/else calling
if iCloudPrivateRelay; then
echo "iCloud Private Relay is: ON"
else
echo "iCloud Private Relay is: OFF"
fiEven though we work really hard to get the plist data extracted we don’t need to walk the entire XML document (you will find PlistBuddy balks at exporting JSON for a number of reasons). Instead we look for the presence of the key name UPDATE: This ambiguity has been resolved and it will now look at the path PrivacyProxyServiceStatus and that is sufficient to reliably detect the state.:$objects:1:PrivacyProxyServiceStatus for the status, which seems to be consistent (LMK otherwise). I have 2 versions in my GitHub iCloudPrivateRelayStatus.sh and the minified one line version iCloudPrivateRelayStatus.min.sh
Limit IP Tracking Status
Limit IP Tracking, is a per-interface setting that is on by default, however has no effect unless Private Relay is enabled. For this we will use ljt my Little JSON Tool to retrieve the value from the massaged JSON conversion of com.apple.wifi.known-networks.plist if on WiFi or if on Ethernet .../SystemConfiguration/preferences.plist. (Update: Now macOS Sequoia compatible after Apple broke the usual way of getting the SSID name for WiFi connections)
#!/bin/bash
: <<-LICENSE_BLOCK
Limit IP Tracking Status Checker (20250204) - (https://github.com/brunerd)
Copyright (c) 2025 Joel Bruner (https://github.com/brunerd)
Licensed under the MIT License
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
LICENSE_BLOCK
#############
# FUNCTIONS #
#############
#include this self-contained function in your script
function limitIPTracking()(
#only for Moneterey and up, 11 and under need not apply
[ "$(sw_vers -productVersion | cut -d. -f1)" -le 11 ] && return 1
#Little JSON Tool (ljt) - https://github.com/brunerd/ljt - MIT License
function ljt () ( #v1.0.8 ljt [query] [file]
{ set +x; } &> /dev/null; read -r -d '' JSCode <<-'EOT'
try{var query=decodeURIComponent(escape(arguments[0]));var file=decodeURIComponent(escape(arguments[1]));if(query===".")query="";else if(query[0]==="."&&query[1]==="[")query="$"+query.slice(1);if(query[0]==="/"||query===""){if(/~[^0-1]/g.test(query+" "))throw new SyntaxError("JSON Pointer allows ~0 and ~1 only: "+query);query=query.split("/").slice(1).map(function(f){return"["+JSON.stringify(f.replace(/~1/g,"/").replace(/~0/g,"~"))+"]"}).join("")}else if(query[0]==="$"||query[0]==="."&&query[1]!=="."||query[0]==="["){if(/[^A-Za-z_$\d\.\[\]'"]/.test(query.split("").reverse().join("").replace(/(["'])(.*?)\1(?!\\)/g,"")))throw new Error("Invalid path: "+query);}else query=query.replace("\\.","\udead").split(".").map(function(f){return"["+JSON.stringify(f.replace("\udead","."))+"]"}).join("");if(query[0]==="$")query=query.slice(1);var data=JSON.parse(readFile(file));try{var result=eval("(data)"+query)}catch(e){}}catch(e){printErr(e);quit()}if(result!==undefined)result!==null&&result.constructor===String?print(result):print(JSON.stringify(result,null,2));else printErr("Path not found.")
EOT
queryArg="${1}"; fileArg="${2}";jsc=$(find "/System/Library/Frameworks/JavaScriptCore.framework/Versions/Current/" -name 'jsc');[ -z "${jsc}" ] && jsc=$(which jsc);[ -f "${queryArg}" -a -z "${fileArg}" ] && fileArg="${queryArg}" && unset queryArg;if [ -f "${fileArg:=/dev/stdin}" ]; then { errOut=$( { { "${jsc}" -e "${JSCode}" -- "${queryArg}" "${fileArg}"; } 1>&3 ; } 2>&1); } 3>&1;else [ -t '0' ] && echo -e "ljt (v1.0.8) - Little JSON Tool (https://github.com/brunerd/ljt)\nUsage: ljt [query] [filepath]\n [query] is optional and can be JSON Pointer, canonical JSONPath (with or without leading $), or plutil-style keypath\n [filepath] is optional, input can also be via file redirection, piped input, here doc, or here strings" >/dev/stderr && exit 0; { errOut=$( { { "${jsc}" -e "${JSCode}" -- "${queryArg}" "/dev/stdin" <<< "$(cat)"; } 1>&3 ; } 2>&1); } 3>&1; fi;if [ -n "${errOut}" ]; then /bin/echo "$errOut" >&2; return 1; fi
)
#sequoia broke the old ways of getting SSID
function getCurrentWiFiSSIDforInterface(){
#no interface, error
[ -z "${1}" ] && return 1
#get the SSID _quickly_ thanks MacAdmins @jby
local currrent_SSID=$(ipconfig getsummary "${1}" | awk -F ' SSID : ' '/ SSID : / {print $2}')
[ -z "${currrent_SSID}" ] && return 1
echo "${currrent_SSID}"; return 0
}
#test interface specified or fallback to default interface
interfaceID=${1:-$(route get 0.0.0.0 2>/dev/null | awk '/interface: / {print $2}')}
#WIFI: key: PrivacyProxyEnabled, file: /Library/Preferences/com.apple.wifi.known-networks.plist
#if no error getting WiFi SSID, then we are WiFi
if wifiSSID=$(getCurrentWiFiSSIDforInterface "${interfaceID}"); then
#key name inside plist
keyName="wifi.network.ssid.${wifiSSID}"
#oddly this file is only read-able by root
if [ ! -r /Library/Preferences/com.apple.wifi.known-networks.plist ]; then
echo "Insufficient preferences to determine WiFi state, run as root" >/dev/stderr
exit 1
fi
#get JSON version, so much easier to get around, convert date and data types to strings
wifiKnownNetworks_JSON=$(defaults export /Library/Preferences/com.apple.wifi.known-networks.plist - | sed -e 's,<date>,<string>,g' -e 's,</date>,</string>,g' -e 's,<data>,<string>,g' -e 's,</data>,</string>,g' | plutil -convert json -o - -)
#if there is NO entry, then it is active, it is opt-out designed
PrivacyProxyEnabled=$(ljt "/wifi.network.ssid.${wifiSSID}/PrivacyProxyEnabled" 2>/dev/null <<< "${wifiKnownNetworks_JSON}")
if [ "${PrivacyProxyEnabled}" = "false" ]; then
return 1
fi
#ETHERNET: key: DisablePrivateRelay, file: /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/preferences.plist,
else
#get JSON, easily converts with not data or date types within
systemConfigPrefsJSON=$(plutil -convert json -o - /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/preferences.plist)
#get current set UUID
currentSet=$(echo "${systemConfigPrefsJSON}" | ljt /CurrentSet 2>/dev/null)
#get value for current default interface of current Location set
DisablePrivateRelay=$(ljt "${currentSet}"/Network/Interface/${interfaceID}/DisablePrivateRelay 2>/dev/null <<< "${systemConfigPrefsJSON}")
#if it is TRUE we are Disabled, then we are NOT ON, return fail code
if [ "${DisablePrivateRelay}" = "1" ]; then
return 1
fi
fi
)
########
# MAIN #
########
if [ ! -r /Library/Preferences/com.apple.wifi.known-networks.plist ]; then
echo "Insufficient privileges to determine WiFi state, run as root" >/dev/stderr
exit 1
fi
#use default interface if nothing is specified for argument $1
interface=${1:-$(route get 0.0.0.0 2>/dev/null | awk '/interface: / {print $2}')}
#returns 0 if ON and 1 if OFF, you may supply an interface or it will fall back to the default
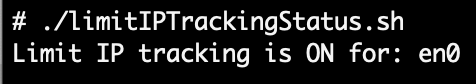
limitIPTracking "${interface}" && echo "Limit IP tracking is ON for: ${interface}" || echo "Limit IP tracking is OFF for: ${interface}"
You can specify an interface or it will use the default interface (there’s a good one-liner to use route get 0.0.0.0 to figure that out). plutil is not initially used to convert com.apple.wifi.known-networks.plist to JSON as it will fail due to XML/plist data types like <date> and <data> that do not have JSON equivalents. First we use sed to change them to <string> types then plutil can convert to JSON. After that it’s a cake walk for ljt to get the value and report back. If the interface is not WiFi then /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/preferences.plist has none of those conversion issues. Check out limitIPTrackingStatus.sh and the minified limitIPTrackingStatus.min.sh at my GitHub.
Thanks for reading! P.S. I won’t be at JNUC 2022, better luck next year!